Understanding The Quantity and Purpose Of IVF Injections: A Comprehensive Guide
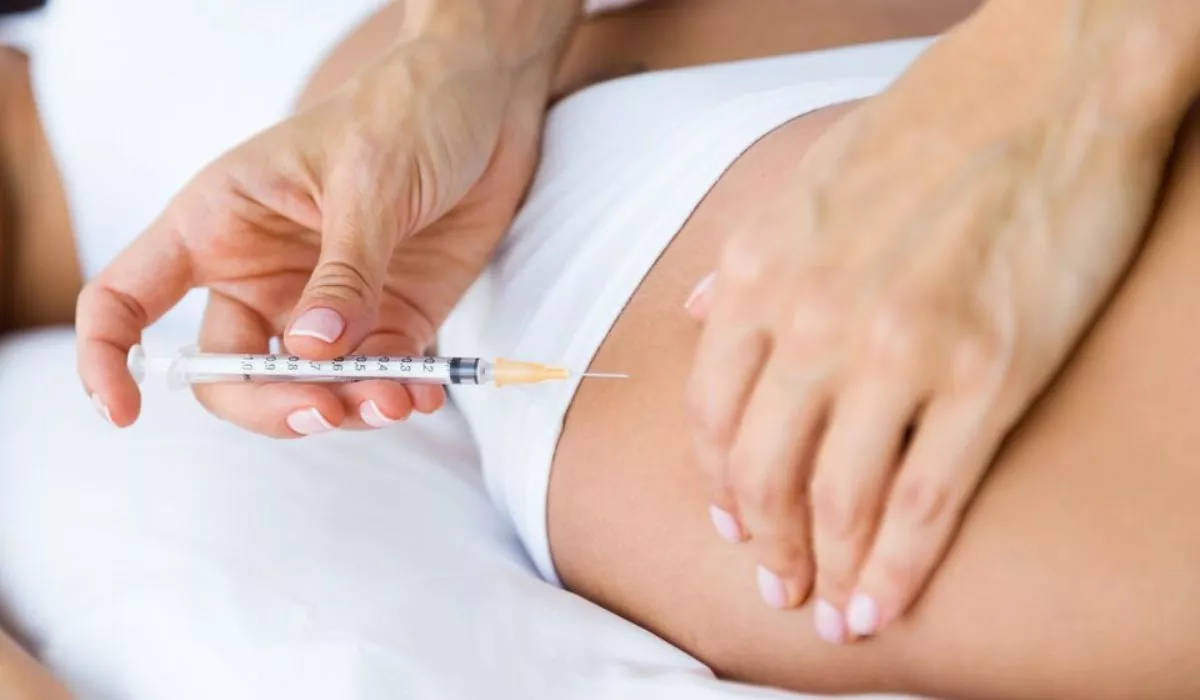
In-vitro fertilization is an assisted reproductive procedure that couples can opt to fulfill their goal of becoming parents. In order to help the woman’s body prepare hormonally for childbirth, many injections are necessary as part of this treatment. IVF cycles require injections at different stages.
It might vary from patient to patient, but throughout the course of the IVF therapy, patients may have up to 80-90 injections (for 10-14 days on average). Furthermore, the patient in question will receive one injection prior to the harvesting of eggs and one following the transfer of embryos.
A woman’s typical menstrual cycle will result in the production of one mature egg every cycle. In order to maximize the chances of a successful IVF procedure, fertility professionals try to gather as many eggs as possible in a single round.
Based on blood tests and ultrasounds, fertility specialists will decide before the IVF operation starts on the length of time, dose, and hormone needs. They will also decide on the frequency and dosage of IVF hormone injections.
The Purpose Of Injections In IVF
Injections are frequently used in IVF for a number of reasons.
Injections play a vital role in the IVF procedure for the following reasons:
- Timing and Monitoring: The injections assist fertility experts in keeping an eye on and regulating when eggs mature. By doing this, the eggs are guaranteed to be collected at the best time of fertilization.
- Avoiding Early Ovulation: A natural cycle may cause the body to release eggs before they are ready to be collected. This may be avoided in order to ensure that the eggs are ready for retrieval.
- Stimulation of Ovaries: The ovaries are stimulated to generate more eggs via injections. A woman normally develops one egg throughout each cycle of her natural menstrual cycle. Having many eggs is necessary for IVF, nevertheless, in order to improve the probability of successful fertilization.
- Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation: It is intended to create many mature eggs at the same time through carefully managed ovarian hyperstimulation. This is important since not every retrieved egg will develop into a viable embryo.
- Encouraging the Luteal Phase: In order to encourage the luteal phase, which is essential for the initial stages of pregnancy should fertilization take place, IVF injections (mainly consisting of progesterone) may be administered following egg retrieval.
- Preparing the Uterine Lining for Embryo Implantation: Several hormone medicines may be employed to make the uterine lining more receptive to the embryo.
These Injections are given under the supervision of fertility professionals and are specifically customized to meet the needs of each person.
Injections Required For IVF
The number of hormones of IVF injections required for in vitro fertilization (IVF) may vary based on an individual’s circumstances. Usually, IVF involves many hormone injections spaced out over ten to twelve days to prime the ovaries for egg retrieval. This procedure aims to produce several eggs for fertilization.
However, the specific number and type of injections may be determined by the fertility specialist based on your individual needs and how you react to the drug. Consulting an IVF specialist is essential for personalized guidance.
To manage and stimulate the reproductive process, several injections are frequently given during In-vitro Fertilisation (IVF) therapy. Usually included in these injections are:
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): This injection encourages the development of several eggs within the ovaries.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): This facilitates the ultimate development of eggs.
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH): This injection controls ovulation.
- Progesterone: Readies the lining of the uterus to implant an embryo.
- Antagonists or Agonists: This is used to stop early ovulation.
Your doctor will assess your unique physical condition to ascertain the precise injections you require, and your treatment plan may change accordingly.
IVF Procedure
Mature eggs are taken from the ovaries and fertilized in an IVF lab with sperm. The primary source of inspiration for the development of the IVF procedure was the shifts in sex hormones that transpire throughout pregnancy and delivery. Following a predetermined IVF injection timetable and monitoring the process continuously throughout is essential.

Injections used in vitro fertilization (IVF) are essential to the procedure. Anticipate many hormone injections to increase the ovaries’ ability to produce eggs. By regulating ovulation time, these injections improve the likelihood of obtaining several eggs for fertilization. The injection site may enlarge, bruise, or cause discomfort. Careful observation by an IVF specialist is necessary to modify the injection schedule and dose. An essential step towards successful fertilization and pregnancy is receiving IVF shots.
The most crucial aspect of ovarian stimulation is IVF injections for pregnancy. The injections are usually administered to the arms, thighs, or belly. This depends on the type of injection that is employed. The injections are thought to be safe and often painless. Unique fine-needled devices may be self-administered and cause little to no discomfort.
IVF Injections and Side Effects
The side effects of IVF injections include the following:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Blurred Vision
- Blisters and Swelling at the Injection Site
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation
Alternative Treatments To IVF Injections
- Intrauterine Insemination or IUI: This technique increases the likelihood of fertilization by having an IVF professional insert specially prepared sperm directly into the uterus.
- Nutritional Therapy: A method of naturally boosting fertility that focuses on a balanced diet, vitamins, and lifestyle modifications.
- Stress Reduction: Reducing stress has a favorable effect on fertility and can be achieved through yoga, meditation, mindfulness, or therapy.
- Changes in Diet and Lifestyle: Fertility can be enhanced by eating a balanced diet and getting regular exercise.
- Egg Donation and Surrogacy: These options may be taken into consideration if the cause of infertility is a problem with the uterus or low-quality eggs.
- Ovulation-Inducing Medications: Clomiphene is one non-IVF medicine that can induce ovulation without needing IVF.
Before considering any treatment it is essential to have a consultation with the fertility doctor to figure out which is the most suitable for you, given your unique health situation. The emotional state of the patient plays a substantial role in the treatment. It is mandatory to remain positive throughout the procedure.
Always follow the prescribed routine by the physician as this can contribute to the overall success of the treatment. Support from the spouse and family can ensure emotional well-being and can enhance the effectiveness of the treatment.
