Is Ovary Size An Important Factor In Getting Pregnant?

The size of a woman’s ovaries has a significant role in reproductive health and affects the ability to conceive.
What is the average ovarian size in centimetres, and how can we determine our personal ovary size?
The typical range of ovarian size and its significance will be discussed in this article.
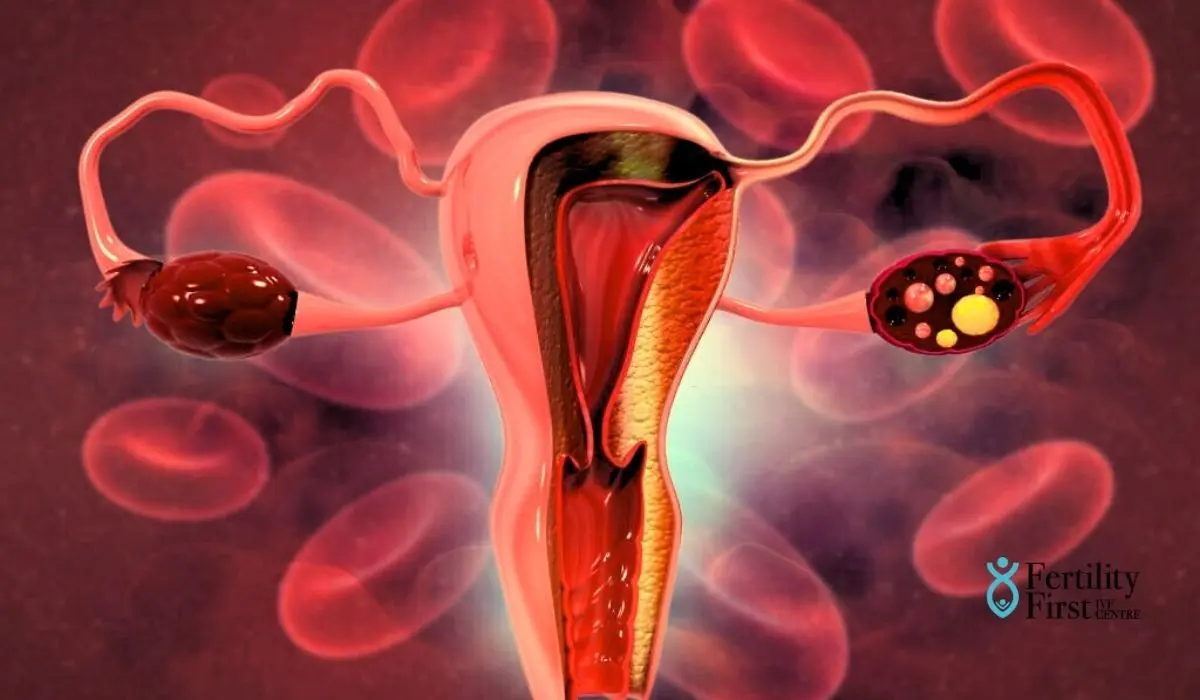
The cervix, fallopian tubes, vagina, uterus, and ovary are among the various organs that make up the female reproductive system. On either side of the uterus, there are two ovaries. The ovaries are tiny, oval-shaped glands that produce and release eggs, also referred to as oocytes. Progesterone and oestrogen are also produced by them.
These processes must be in order for a woman to have healthy reproductive organs and be fruitful.
When an embryo is almost 8 weeks old, the ovaries start to develop inside the womb. Your ovaries change during the course of your life, much like any other organ in your body.
There are two ovaries present at birth, each measuring 1 cm in diameter and weighing between 250 and 350 mg. The ovaries do not produce new eggs.
Factors That Affect Ovary Size During Pregnancy
The size of the ovary is influenced by a number of variables. Your ovaries’ size and shape may alter over time as a result of medical issues or ageing.
The following are common factors that influence ovary size:
How are ovaries measured for size?
Your doctor will attempt to measure your ovarian size to find the problem if you are having trouble getting pregnant. He or she may request certain laboratory procedures and examinations to observe and evaluate the condition, effectiveness, and amount of the ovaries.
The following are typical examinations used to gauge ovarian size: Ultrasonography (USG) & blood tests
How important is ovary size during pregnancy?
Your chances of becoming pregnant may be affected by irregular ovarian size.
Small ovaries might make it more challenging for women to get pregnant because they can influence follicular growth, which in turn affects the ovulation process.
However, larger ovaries may also affect your ability to conceive. The reason for this is that having larger ovaries does not necessarily mean having more ovarian follicles. Usually, hormonal imbalances and cystic tumours are to blame for the enlarged size of the ovaries. Your ovaries can grow to a maximum size of 15 cm.
For pregnancy, it’s crucial to get the ovary to a normal size.
The ideal ovarian size is 3 cm by 2.5 cm by 1.5 cm.
What impact does ovarian size have on the effectiveness of fertility treatments?
Ovarian size can have an impact on the success rate of fertility treatments since smaller ovaries are associated with lesser egg reserves, which make conception more challenging.
IVF success rates: The reason for poor ovarian reserve, the number of eggs a woman has, and how her body reacts to fertility treatments all affect how successful IVF is. The quantity of eggs retrieved during IVF may be impacted by a woman’s smaller ovaries’ potential for a lesser response to ovarian stimulation drugs. A successful fertilisation and embryo transfer can occur in some women with smaller ovaries since they may still have high-quality eggs.
For women aged 35 and older, the combined per-cycle pregnancy rates for clomiphene and intrauterine insemination are 8.2%. A reduced response to clomiphene, which induces ovulation, and intrauterine insemination, which involves injecting sperm directly into the uterus, may be observed in women whose ovaries are smaller.
How can the size and condition of ovaries be improved?
There are several techniques to increase the size and health of the ovaries, which can increase the likelihood of getting pregnant.
The following are suggestions to enhance ovarian health:
Keeping a healthy weight in mind Both being overweight and underweight might interfere with ovulation and lessen the likelihood of becoming pregnant. Body mass index (BMI) ranges from 18.5 to 24.9 for a healthy person.
Body mass index (BMI) ranges from 18.5 to 24.9 for a healthy person.
Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a diet rich in leafy greens, whole grains, lean meats, nuts, fresh produce, and fruits helps enhance fertility and general health. Avoid processed meats, refined carbohydrates, trans fats, and a lot of salt and sugar.
Regular exercise can improve blood flow generally, enabling the ovaries to receive more oxygen and nutrients. Exercise also lessens stress, which has been shown to affect fertility.
Control your stress: Excessive stress might interfere with ovulation and lessen your chances of getting pregnant. Improved ovarian health can result from stress management practises like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
Boost blood flow: The health of the eggs depends on oxygen-rich blood flowing to the ovaries. Yoga poses including the lotus, child, and reclining hero help increase blood flow to the ovaries, as can drinking lots of water, being hydrated, and practising these poses.
Conclusion
Ovarian size affects a woman’s capacity to become pregnant and sustain a healthy pregnancy. A decreased egg reserve is indicated by smaller ovaries, which can make conception more challenging. Oestrogen and progesterone, which are essential for supporting pregnancy, are also produced by the ovaries.
An ovary typically measures 3.5 cm by 2.5 cm by 1.5 cm, though size varies with age. Before puberty, ovaries are less than normal in size; they then get larger during puberty and finally reach their largest size during pregnancy.
The size of the ovaries starts to decline around 35 years, and after menopause, they get smaller.
The effectiveness of reproductive treatment can also be influenced by the size of the ovaries.
However, altering one’s lifestyle to incorporate activities like eating a balanced diet, working out frequently, managing stress, improving blood flow, and considering supplements might aid in improving ovarian health and increasing the likelihood of getting pregnant.
