How long does birth control stay in your system?

Birth control is an essential aspect in the life of an adult, whether it’s taken as an emergency contraceptive or it’s a long-term one for planned parenthood. It’s totally normal to have confusion and doubts regarding the birth control methods, which one to take, and several other doubts, like side effects and how long it will stay in your system.
What is birth control, and how does it work?
The methods or devices that are used to prevent pregnancy are generally called birth control. The modern birth control techniques were devised in the 20th century, and the process of using birth control is called family planning.
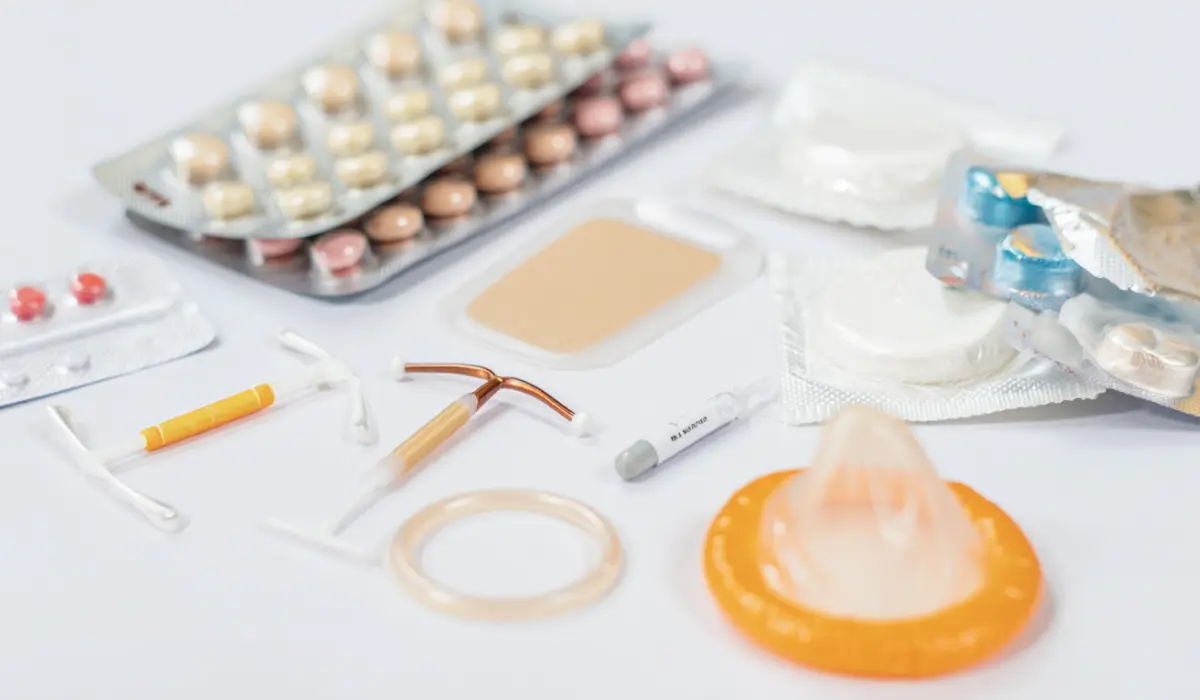
There are many birth control techniques, from long-term to temporary, from oral contraceptives and barrier methods, which work temporarily, to more long-term ones like contraceptive implants.
The hormonal method works by interfering with the ovulation cycle and other biological methods by altering the hormonal aspects. These include the emergency contraceptive pill and Certain IUDs
The barrier method works by creating a physical blockage to stop fertilization. The common methods of the barrier include condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps. The barrier methods also offer protection against Sexually transmitted infections and diseases, which is an upside when compared to other hormonal contraceptives.
Barrier methods typically have no side effects, while the hormonal ones do alter the biology of the user. Hormonal ones often leave a trace and stay in the body for a time before the effects wear off. The presence of birth control in your body depends on the type of contraceptive you used
How does the hormonal birth control work?
Hormonal birth controls typically work because of a combination of two hormones; most of the hormonal contraceptives contain at least one of the hormones.
Estrogen
Estrogen is naturally seen in humans, is one of the important components of the hormonal birth control. The estrogen suppresses the production of FSH(Follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone)> FSH is responsible for developing the ovarian follicles, which contain the eggs, and LH is responsible for the release of the eggs. Estrogen in the birth control suppresses both these hormones. This prevents ovulation.
Progestin
Progestin is a synthetic form of the naturally occurring progesterone hormone. It prevents pregnancy via different primary mechanisms. It thickens the cervical mucus so the sperm won’t be able to enter that barrier. It can also thin the lining of the uterus. And it slows the movement of the egg through the fallopian tube.
Most of the Hormonal birth controls primarily work by preventing ovulation, thinning the uterine walls, and making the cervical mucus thick. This method of contraception typically has a higher success rate than the normal barrier method, but also comes with certain side effects.
How long does a hormonal contraceptive stay in your system?
The amount of time a hormonal contraceptive stays in your system might vary depending on the kind of birth control you are on
Contraceptive pill
There are two types of contraceptive pills:
- Combination pills(COCs)
- Progestin-only Pills (POPs)
Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin. They suppress the mid-cycle surge of the LH and FSH and prevent ovulation, while POPs primarily rely on thickening cervical mucus to block sperm and also suppress ovulation to an extent.
The degree of suppression varies according to different POPs. The Contraceptive pills typically clear themself from the body within 48 hours. And the menstrual cycle and the body hormones will return to normal within three months.
Intrauterine device
An IUD is a small contraceptive device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. There are two kinds of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal.
A non-hormonal IUD is made of copper; the copper ions, which are toxic to sperm, will keep the sperm at bay and create an environment that is toxic to them.
The hormonal IUD releases a small amount of progestin into the uterus.
The Effects of the Hormonal IUD will be gone when you remove it from your body, and the menstrual cycle and the other hormones will be back to normal within two months after the removal of the IUD
Contraceptive Implant
The implant is a small hormonal contraceptive that slowly releases the hormone progesterone over a long period of time, and it is typically inserted under the skin of your upper arm. The insertion is a small process that can be done by a healthcare professional.
The upside of using an implant is that fertility returns quickly, and pregnancy can occur as soon as the implant’s effect wears off. In most cases, the system is clean within a week, and the menstrual cycle will return to normal within a month of the removal.
Contraceptive Shot
The contraceptive shot is a dose of progestin that prevents pregnancy for three months. It is highly effective and reversible, it’s estrogen-free, so it is a suitable option for those who cannot use estrogen-based contraceptives.
After stopping the shot, it remains in the body for about three months and may take up to 18 months for the periods to come back to normal.
Contraceptive Ring
A contraceptive ring is a small, flexible ring that can be inserted into the vagina to prevent pregnancy. It releases a small continuous dose of hormones, which are then absorbed through the vaginal wall to the bloodstream.
The effects of the ring will stay for 48 hours after its removal, and it will take three months for the functions to return to normal.
Contraceptive Patch
The contraceptive patch is a small band-like patch that is worn on the skin and releases hormones to prevent pregnancy. It delivers a continuous dose of estrogen and progestin into your bloodstream through the skin.
The body will have traces of the patch for about 48 hours after the removal, and it might take three months for the menstrual cycle to come back to normal.
| BirthControl Method | How long it stays in the body | Time for normal cycle to return |
|---|---|---|
| The hormonal IUD | Until removal | Up to two months |
| Contraceptive Pills | Protective for 48 hours after taking | Up to three months |
| Contraceptive ring | Protective for 48 hours after removal | Up to three months |
| Contraceptive patch | Protective for 48 hours after removal | Up to three months |
| Contraceptive implant | Protective for 7-14 days after removal | Up to three months |
| Contraceptive shot | Protective for three months after injection | Up to 18 months |
Can you get pregnant with birth control in your body?
In most cases, the birth control will only offer protection for 48 hours. Still, in many cases, the body will not be ready for pregnancy yet.
If you are trying to conceive, then it’s crucial to plan and chart the fertile period, especially if your body has been going through hormonal contraceptives. A contraceptive injection or shot is the only birth control that causes a delay of more than a year.
In most cases, the hormonal contraception works by altering the menstrual cycle, and it takes about 90 days for the typical cycle to return and for the whole altered physiology.
Also, 90 days is enough for an ovarian follicle to mature into the ovulation stage.
IF your cycle is abnormal even after the 90 days, then you need to seek medical attention as soon as possible because there might be an underlying issue at play.
And above all, remember that it is your body, make informed decisions regarding your health, and when in doubt, always consult an expert
Can birth control cause infertility?
No, birth control does not cause infertility. Most hormonal and non-hormonal contraceptives are designed to temporarily prevent pregnancy, not to affect your long-term fertility. Once you stop using birth control, your body gradually returns to its natural hormonal rhythm, and ovulation resumes.
For most people, fertility returns within a few weeks to a few months, depending on the type of contraceptive used. The only exception is the contraceptive shot, which may delay the return of fertility for up to 18 months after the last injection.
However, this delay is temporary and does not mean permanent infertility. If you notice that your menstrual cycle does not return to normal even after several months, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider to rule out any other underlying conditions.
