Unlock Your Fertility Potential: Fallopian Tube Reversal Explained – Interactive Guide
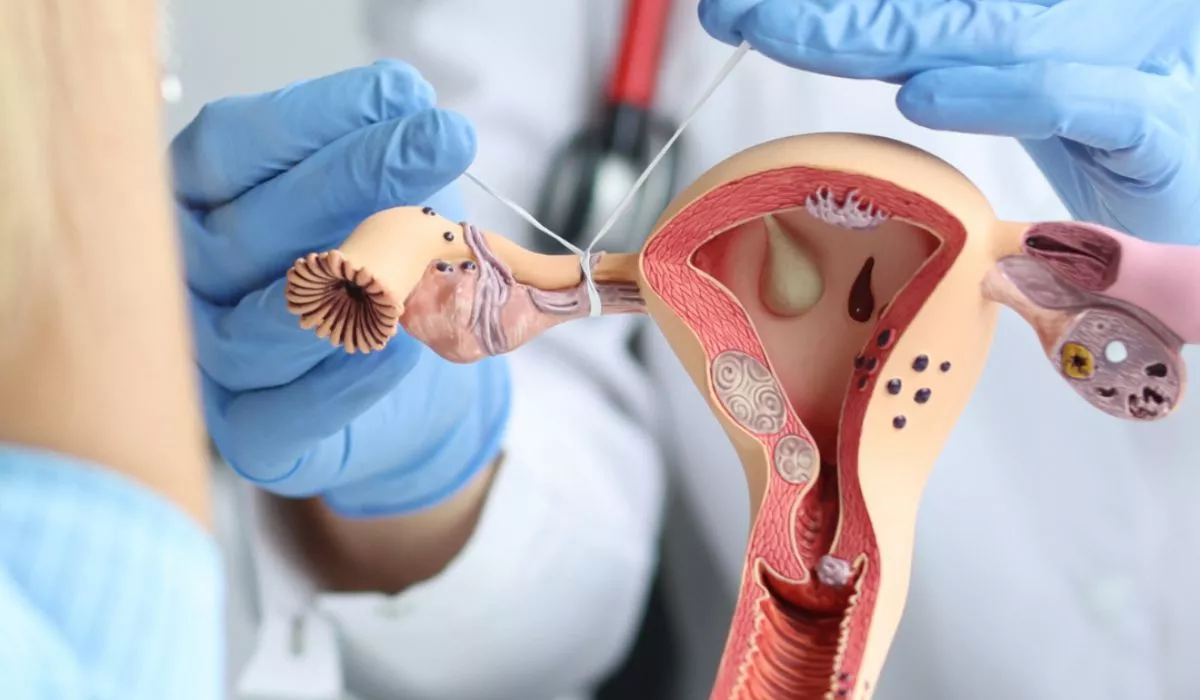
Fallopian tube (tubal) reversal is a surgical treatment that reopens or reconnects the fallopian tubes following tubal ligation, a female sterilization method. This technique is intended to restore fertility and allow women to conceive naturally.
What Is Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation is a female birth control procedure. To prevent pregnancy, the Fallopian tubes are clamped or sealed. A woman’s egg must travel via the Fallopian tubes to meet the sperm before entering the uterus after fertilization. The flow of the egg is halted once the Fallopian tubes are tied off, resulting in sterilization.

Women who have previously had tubal ligation may opt to conceive again. Tubal reversal surgery is one option for accomplishing this. A tubal ligation reversal reconnects the obstructed parts of the Fallopian tubes, allowing the eggs to pass through.
A woman may undergo a tubal reversal for a variety of reasons. Tubal ligation at a young age, a change in marital status, and an imperfect understanding of tubal ligation are all plausible causes for requesting a reversal surgery.
Here Are Some Important Factors To Remember About Tubal Reversal And Its Influence On Fertility:
Tubal ligation reversal is reconnecting or reopening fallopian tubes previously occluded, cut, or sealed during tubal ligation. Several factors influence the procedure’s success, including the type of tubal ligation utilized, the length and health of the remaining fallopian tubes, and the patient’s overall health.
By reopening the fallopian tubes, tubal reversal permits eggs to flow from the ovaries to the uterus, where fertilization can occur. This procedure enables women to conceive naturally without needing IVF or other assisted reproductive technologies.
- Alternatives: Women can consider alternatives like IVF, where the fertilization process takes place outside the body, and the embryos are then transferred to the uterus if tubal reversal is not possible or not advised. Pregnancy with IVF does not require open and functioning fallopian tubes.
- Long-term risks: Tubal reversal may occasionally fail to produce a live birth, and women may continue infertility even after the procedure.
Before deciding, speaking with a healthcare expert about tubal reversal’s potential risks and benefits is important.
Procedure
Tubal ligation reversal requires abdominal surgery and can be performed as an inpatient or outpatient operation lasting one to three hours. General anesthesia is required for the surgery.
Tubal ligation is reversed by making a small incision in the abdomen (mini-laparotomy or laparoscopy) to reach the reproductive tissues. A microscope-guided or laparoscopic-guided operation will remove the blockage in the Fallopian tubes and reunite the remaining tubal structures with absorbable stitches.
A dye is injected into the tubes to ensure that tubal reconnection is successful. The Fallopian tubes have varying diameters depending on how far they extend. The highest probability of success is to link two pieces of the tube with identical diameters.
The Fallopian tubes are normally 8 inches long, and women with at least 4 inches of the tube after the re-joining process have the highest pregnancy success chances following a tubal reversal procedure. This surgical treatment necessitates specialized equipment and is best conducted by highly trained surgeons.
Following surgery, recovery normally takes 2 to 3 weeks. Meanwhile, the incision areas must remain clean and dry. During healing, strenuous activity, intercourse, and the use of aspirin must be avoided. Infections, blood loss, harm to neighboring organs, and anesthetic side effects are all risks of this sort of surgery.
What Are The Rates Of Success For Tubal Reversal Surgery?
The length and health of the remaining fallopian tubes, the type of tubal ligation, the patient’s age, and other factors influence tubal reversal operation outcomes. The following are some expected success rates:
- Pregnancy Rate: After reversing a tubal ligation, the likelihood of getting pregnant might range from 50% to 80%. Another study discovered a 70% success rate for pregnancy within 18 months following surgery.
- Delivery Rate: It is anticipated that the delivery rate after tubal reversal surgery ranges between 52.7% and 75.3%.
- Age Factor: Tubal reversal is more common in younger women. A study of women over 40 who had tubal reversal found that the pregnancy and live birth rates were 25% and 19.2%, respectively.
- Ectopic Pregnancy Risk: According to one study, 4% and 8% of women who had a sterilization reversal operation experienced an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancies can be fatal and necessitate quick medical intervention.
Is Tubal Reversal Surgery Associated With Any Long-Term Consequences?
Tubal reversal surgery has risks and potential long-term consequences like any other surgical operation. Here are some of the long-term consequences of tubal reversal surgery:
- Changes in Menstruation: Some women may experience irregular menstrual periods for 1 to 2 months after surgery.
- Ectopic pregnancy risk: There is an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy after tubal reversal surgery, in which the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. This is because the treatment may cause scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes, increasing the chances of the egg becoming trapped in the tube.
- Scar Tissue Creation: Surgery can produce scar tissue, impairing fallopian tube function and raising the risk of future reproductive problems.
- Recurrent Tubal Ligation: Following tubal reversal surgery, the fallopian tubes sometimes become blocked once more, causing infertility to return.
Before deciding, discussing the potential risks and benefits of tubal reversal surgery with a healthcare professional is important. Alternative options, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), should also be considered, as they may be more suitable for some women.
Conclusion
After tubal ligation, a method of female sterilization, the fallopian tubes are surgically opened again. This surgery is known as tubal ligation reversal. This surgery attempts to restore fertility in women who have had tubal ligation and wish to conceive again. The effectiveness of tubal ligation reversal in assisting a woman to conceive depends on several variables, including the type of ligation therapy, the condition of the fallopian tubes, and the woman’s age.
It’s essential the success of tubal ligation reversal in establishing pregnancy might vary based on numerous circumstances, including the type of ligation treatment, the state of the fallopian tubes, and the woman’s age. In other circumstances, IVF may be a better alternative for achieving pregnancy because it does not require the fallopian tubes.
